
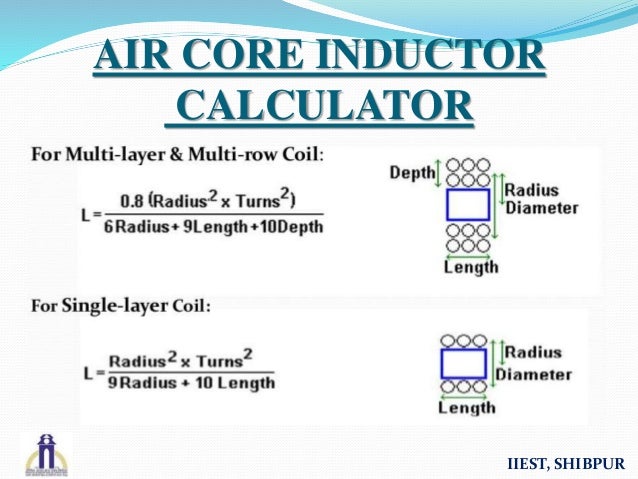
(This formula was corrected Apthanks to KB!) Here it is in terms of D, the diameter of the coil: L = inductance in micro-Henries (not nano-Henries!) The classic formula for single-layer inductance (air core) is called Wheeler's formula, which dates back to the radio days of the 1920s: The graphic below was contributed by Sebastiaan. The most useful (read that "highest Q") solenoids for microwave applications are miniature, single-layer air-core inductors.
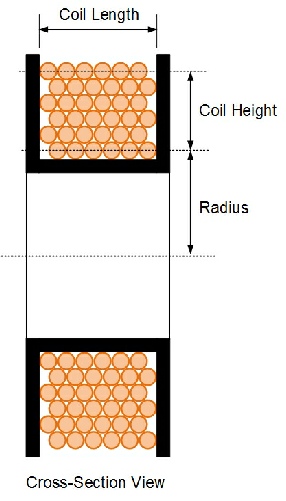
It can have a single layer of windings, or multilayer, and it can use an air core or a core with high magnetic permeability for increased inductance. Luckily all of those decimal places just cancel each other out!Ī solenoid is a cylindrical shape that is wound with wire to create inductance.
#Single layer air core inductor calculator series
On the Smith Chart, this means that series inductance tends to move a reflection coefficient in a clockwise direction.Ī more useful form of the inductive reactance equation is given below, where frequency is in GHz and inductance is in nanohenries. Note that inductive reactance is positive, the opposite polarity of capacitive reactance. The well-known equation for inductive reactance is shown below. Use our reactance calculator if you are interested in this topic! Wirebond inductance (now on a separate page) Spiral inductors on a substrate (New for March 2016!) Inductance of a transmission line (separate page) Thanks, Keysight!īelow is an index of our mathematical discussion of inductors:
#Single layer air core inductor calculator how to
Click here to go to our main inductor pageįor March 2016, our friends at Keysight Technologies gave us a video on how to model spiral inductors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
